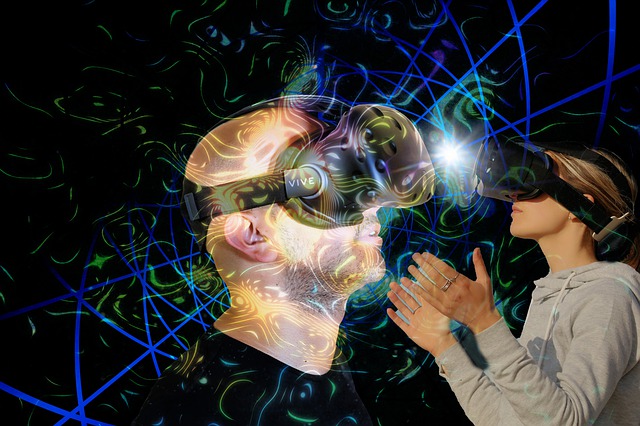
Augmented reality is an experience where the real environment is modified by computer-generated objects to enhance a user’s physical world.
The job of designers is to create inputs, which could run the gamut from GPS overlays and graphics to video and sound, and these inputs adapt in real-time to the user’s environment.
Have you tried to catch a Pokémon, tried on Makeup on the L’Oreal website, or tried to fit virtual furniture in your room via the IKEA app? If so, you have already had a brush with this amazing technology.
In essence, augmented reality technology adds an additional layer of information to our physical world. In contrast to Virtual reality which replaces entire actual environments with digital ones, AR seeks to superimpose those computer-generated images into our physical world, thus altering our perception of reality.
Though you may have got to grips with simple AR entertainment applications, such as Harry Potter wizards united, Pokémon Go, Google’s AR animals, and Snapchat filters, AR is being applied in far consequential uses to impact our habits, social life, and the entertainment industry.
For instance, most cars these days are fitted with AR “heads-up” displays that put collision warnings, navigation, and other information directly in driver's lines of sight. Similarly, thousands of companies are making factory workers wear AR devices that superimpose service instructions or manuals.
Perhaps overlaying scores to live-feed sports events is the biggest support that augmentation is happening in real-time. Some popular augmented reality applications include:
- Holographic glasses allow doctors to visualize organs in 3D during a surgical intervention.
- Recognizing a person's face and discovering all the social networks on which they have a presence.
- Direct your mobile’s camera to the sky, and you will be able to map out planets, constellations, stars, and other celestial bodies, as well as know more about them.
- Architectures can enable clients to check in real-time how their house will look once the work is completed or how a particular furniture or color will fit in with the rest of the decor.
- From virtually trying on foundations to clothes, AR is all set to give a new meaning to experiential shopping.
- Travelers can point their phone’s camera to anything written in a foreign language and have it translated in real-time.
- Mountaineers and cyclists can explore their routes in 3D by projecting them into any surface.
- Buyers can envisage their future car and have it tailored to their tastes and needs.
How does Augmented Reality work?
Most of us want to go behind the scenes and see how the magic works. Augmented reality technology uses a wide range of data, including 3D models, animations, images, and videos, but the users are always aware of being in the real world.
For AR to work, it requires a range of technologies such as depth tracking, simultaneous localization, and mapping, as well as Cameras and sensors to collect data about user interactions and the current environment, in order to better understand what is in the world around the user.
The cameras on your AR device, be it smartphone cameras or specialized special-duty ones, continue to scan your surroundings and send this information for processing.
This data is used by the device to locate physical objects and generate 3D models. AR machines receive this data and process it just like a mini-computer. This is why, they also need Bluetooth/WiFi, RAM, flash memory, a GPU, a CPU, and a GPS to measure orientation in space, direction, angle, speed, temperature, and so on.
Certain specialized AR headsets are fitted with a miniature projector that takes data from sensors, processes it, and projects digital content onto a surface for people to view.
Types of Augmented Reality
There are primarily four types of AR. First, we have Marker-based AR, in which a special visual object (a trigger object), such as a special sign or a QR code, needs to be scanned by a camera.
The AR device also needs to determine the orientation and position of a marker in order to position the content prepared in advance at a precise place. For instance, in order to display an educational animation right onto some paragraph on some page, we need to know that the user is pointing the camera at that particular place.
On the other hand, imagine augmented reality applications that help you visualize how a virtual furniture piece will look inside your bedroom.
You can try any number of different combinations of styles, orientations, and locations, and you get to decide where to place the virtual object. This is what we call a “markerless AR” or location-based AR. This form of augmented reality employs an accelerometer, a gyroscope, a compass, and a GPS to locate the user’s pointer.
We also have Location-based AR which correlates AR content to a specific location. Imagine walking down an unfamiliar street in a new city, and suddenly your phone’s camera shows you a virtual road sign displaying the street name. This is what location-based AR is all about.
With the availability of smartphones, this type of AR is able to produce near-by business ads pop-ups, nearby businesses info, and even directions and maps.
Next up, we have projection-based AR, in which synthetic light is projected to physical surfaces and users can even interact with it. Remember the holograms in Star wars? They don’t seem so futuristic now, do they? These devices detect user interaction with a projection by its alterations.
Last, we have super-imposition-based AR, in which, the original view is partially or completely covered by the AR. This whole concept is only possible due to object recognition. A great example of this is the IKEA Catalog app, which allows users to place virtual furniture items from the catalog in their rooms, in order to see if the size and style fits.
Augmented Reality Devices
A lot of devices support augmented reality technology, from your average tablets and smartphones to more advanced gadgets like handheld devices and Google Glass, and more are yet to come.
Augmented reality tools and hardware need to process and project data, for which they need CPU, GPS, digital compass, gyroscope, accelerometer, cameras, and sensors. Perhaps, the most common devices suitable for AR are your mobile devices that can run AR mobile apps, such as those for social networking, sports, business analytics, gaming, or entertainment.
In addition, a lot of special AR devices sorely offer advanced augmented reality experiences, such as head-up displays (HUD), which transmit data to a transparent display directly in the viewer’s line of view. Even though this gear was first invented to train military fighter pilots, they are fast becoming popular in sports, manufacturing, the automotive industry, and aviation.
In addition, AR glasses, such as Laforge AR eyewear, Laster See-Thru, Meta 2 Glasses, and Google Glasses, let you access content hands-free, provide real-time instruction to assembly line workers and surgeons, let you see directions on the road, and allow you to see notifications from your smartphone.
Smart lenses are another way to amp up your augmented reality experience. Samsung and Sony are already in the throes of producing them, and so are other technology giants.
To take AR even one step further, we have Virtual retinal displays, which directly project laser light into the human eye to create bright, high-contrast, and high-resolution images. However, these devices are not available commercially so far.
Using AR for Better Customer Experience
The only reason people still prefer brick-and-mortar stores over online shopping is that they want to try products before purchasing them.
This is what automobile test drives, cosmetic samples, and fitting rooms are for. Augmented shopping is no doubt revolutionizing the online experience for customers.
Using AR, prospective customers can virtually try on clothing, makeup, and see how a particular piece of house décor will look inside their rooms, without ever physically interacting with them.
This alleviates brands from having to stock a large inventory just for sampling and means that customers can try on a dozen shades of lipsticks without ever having to visit the store.
L’Oreal’s ‘Style My Hair' app lets users give themselves virtual makeovers, in order to see how a hair dye will look before purchasing. Thanks to its facial recognition tech, Sephora lets you try on various shades on your face in real-time and even compare looks for a better idea.
AR can also be used to provide after-sales services so that customers can avoid the customer service staff altogether, For instance, Using an AR app, customers can get an in-depth self-service overlay, such as resources like FAQ pages and help sheets, by just pointing their phones at the product.
Mercedes has an ‘Ask Mercedes’ virtual assistant, through which drivers can get detailed info on the functionality of any element by pointing their phone at it. Nespresso lets users scan their packaging and instantly see step-by-step coffee machine descaling instructions on their phones.
AR is also being employed in interactive packing to provide excellent customer service at the point of sale. Customers can point their phones at a product's packaging and enjoy fun facts about the products, interesting information, and compelling visuals.
For instance, Heinz uses this technology to provide useful, practical insights about different products. If you point your phone at a Heinz ketchup, you can see a range of recipes that use tomato ketchup.
AR technology is also being used to report faults in a product. Customers don’t often understand a product and find it hard to actually explain to the customer representative what isn’t working.
However, AR technology allows customers to hold their phone up to a broken product and have the broken part explained to them in real-time. That will make it easier for a customer to report what went wrong.
Augmented Reality in Gaming
Gaming is another area where AR is making big waves! The rapid growth of AR-based game development has caused an increase in engaging games and more immersive experiences for users.
Augmented reality lets developers create the ultimate 3D experience for the users, who feel that they are interacting personally with their digital environment.
AR games appeal more to the younger generation since adds a digital layer to their existing real-life setting and make them feel like they are a part of the game.
AR games are introducing new innovations and creativity, and look ready to bid adieu to all the traditional gaming systems like PlayStation, Nintendo, and Xbox with new techniques and trends. For obsessive gamers and developers, AR technology is going to create endless possibilities in gaming.
Perhaps, Pokémon Go, the biggest mobile game ever, is the best example of augmented reality in gaming. The game has you going out into the real world, on the streets you have frequented, only this time, you will be capturing Pokémon, visiting battle Gyms, hitting up Pokestops, and completing missions with actual people.
Similarly, Microsoft has announced Minecraft Earth, a promising new AR game which will bring the blocky construction set into the real world.
Imagine being able to build things directly on your desk or kitchen table or even place your finished buildings anywhere you want on earth.
You may also have heard of ‘Harry Potter: Wizards Unite’, the Niantic’s latest AR game. It works along the lines of Pokémon Go; Players walk around the real world, battle foes, complete missions, collect various things, and so on.
Players group with others to deal with some calamity or other that has affected wizards everywhere, and need wizards to work hand in hand. What more could a Harry Potter fan ask for.
AR In Dubai Mall
Dubai mall recently launched a futuristic virtual and augmented reality park, with an amazing range of AR/VR games, an out-of-this-world roller coaster experience, and plenty of experiential attractions. Some of the most popular attractions include The Walking Dead and the John Wick Chronicles.
Also, most families are attracted to Arena, a studio that brings photo-realistic characters into the real world with the help of AR. Sports aficionados can also try their hand at a lot of games, such as golf, football, hockey, and virtual boxing.
Want to Sky dive but afraid of heights? ‘Plummet’ gives you the ultimate skydive experience, allowing you to drink in the sights and sounds of Dubai, without actually doing the act.
There is even a VR carousel aimed at children aged 3 and over, and a lot more. The best part, you can be propelled down the side of Burj Khalifa, world's tallest building, virtually of course, and see what It’s like to fall down 7,000sqm!
Corporate Training
Virtual and augmented reality are commonly used in corporate trainings by simulating real world situations.
AR enables immersive training without leaving the workplace, and since hands-on learning is more effective for many learners, workers will be able to virtually work on complex tasks without any real hazard.
For instance, factory workers can test their knowledge safely using AR devices and even receive real-time assistance on tasks, without risk of injury.
In a nutshell, AR technology can turn theoretical lessons into practical lessons. Tyson Foods, witnesses a 20% drop in their reported workplace injuries after turning to AR technology in their corporate training.
Maintenance specialists will be better able to work on high-voltage equipment with the help of information offered by specialists and software.
This makes sure that even ordinary technicians can conduct timely maintenance at a high level without having to retrain them from scratch. Everything that they need to know is available through their AR helmet or glasses, and all the information is kept relevant and up-to-date.
See-What-I-See (SWIS) AR smart glasses, in particular, are best suited to help workers get real-time remote assistance from more skilled and qualified experts without having to call them on the site, whenever a complex or non-standard issue crops up.
For instance, Boeing technicians use their AR headsets to receive a step-by-step maintenance checklist, when working with electricity plane equipment. This leaves no room for error during maintenance and cuts down the maintenance time.
NASA is also jumping on the augmented reality bandwagon to teach its workers troubleshooting and maintenance in outer space.
International Space Station workers will be able to virtually see helpful data that simplifies diagnostic procedures and repairs.
AR in schools
As with every other field, AR is generating quite a buzz in the education sector as well. With the help of AR, teachers are able to create three-dimensional models of almost any object, which aids in learning, as well as keeps the students engaged.
Not to mention, these models are interactive and dynamic, which offers a truly immersive experience to students. With the help of AR, students will be better able to grasp concepts such as our solar system, the circulatory system of the human body, or even a hatching hurricane. With AR, noting is impossible, be it natural phenomena, chemical compounds, galaxies, or dinosaurs – anything can be made into a 3D model to enhance the grasp of the topic at hand.
The best part is that all those objects can be manipulated by hand gestures; students can zoom in or out, rotate the object, move it around, and not mention, actually gauge the shape, size, and relative position of objects. Look at the ‘Aug That!’ augmented reality application, which includes tons of excellent AR courses aimed at making elementary school students love learning.
What is Augmented Intelligence?
Augmented reality is an experience where the real environment is modified by computer-generated objects to enhance a user’s physical world.
The job of designers is to create inputs, which could run the gamut from GPS overlays and graphics to video and sound, and these inputs adapt in real-time to the user’s environment.
Have you tried to catch a Pokémon, tried on Makeup on the L’Oreal website, or tried to fit virtual furniture in your room via the IKEA app? If so, you have already had a brush with this amazing technology.
How Augmented Reality software and tools work?
AR software works by connecting to devices such as specialized headsets, phones, and headsets. These integrating devices contain digital projectors, sensors, and a host of other software that enables these computer-generated objects to be projected into the real world.
What Is The Concept Of Augmented Reality?
You can think of augmented reality as an enhanced version of the real physical world, projected onto our existing reality, which is achieved through various digital visual elements, sound, as well as other sensory stimuli delivered via technology.
Designer-generated input, such as GPS overlays, sounds, images, and sound, are capable of responding in real-time to changes in the user’s environment, typically movement.